Guide
Vapor extraction systems for hot cutting of polystyrene foam
Occupational safety in hot polystyrene foam cutting is a topic that is often downplayed, especially by those new to foam material processing. The fumes produced during the melting of polystyrene foam contain substances that can affect health with prolonged exposure. Proper ventilation of the workplace is a basic requirement to ensure comfortable and safe conditions. Take care of your health and learn how to effectively protect your workstation from harmful fumes!
Dlaczego wentylacja to podstawa przy cięciu styropianu na gorąco?
When polystyrene foam is melted at high temperatures, vapors containing particles of the melted polymer and its thermal decomposition products are produced. In small quantities and with short-term exposure, they do not pose an immediate danger, but they Working for hours in a room without adequate ventilation leads to an accumulation of substances in the air. The result can be irritation of the respiratory tract, a feeling of shortness of breath or headaches.
A professional approach to organizing a workstation involves exhausting vapors directly from their source. W Pro-Cut We offer equipment designed to minimize fume emissions and provide comfortable working conditions. Such an investment pays off through improved operator well-being and the ability to work longer, more efficiently without discomfort.

What actually goes up in the air with thermal cutting?
Hot cutting Generates several types of air pollutants. The main component of the vapor is fine particles of melted polystyrene, which float as a white mist. In addition, products of incomplete thermal decomposition of the polymer - mainly styrene, which has a characteristic sweetish odor noticeable even in low concentrations - are generated in small amounts.
The cutting temperature has a direct effect on the type and amount of vapor produced. The optimum temperature for EPS polystyrene is. 250-300°C - The material melts cleanly with minimal emissions. Overheating to 400-500°C significantly increases the amount of fumes and decomposition products. Therefore, temperature-controlled equipment not only allows for better cutting quality, but also reduces air pollution.
What are polystyrene fumes and are they dangerous?
Styrofoam vapor is a mixture of fine particles of molten polymer and volatile organic compounds. The primary component is styrene - A chemical compound used in the production of polystyrene. In low concentrations, typical of occasional cutting in a well-ventilated space, it does not pose a serious health risk. Problems arise with prolonged daily exposure in poorly ventilated spaces.
Symptoms of overexposure to vapors:
- Irritation of the eyes and upper respiratory tract - burning, tearing, coughing
- Headaches and dizziness - especially after several hours of work
- Feelings of fatigue and weakness - difficulty concentrating
- Nausea - in case of very intensive exposure
People with asthma, allergies or respiratory diseases should take special care and ensure increased ventilation of the workplace. For occupational exposure to vapors, consider using masks with dust filters that limit the inhalation of fine particles.
Basic workshop ventilation - what do you need to know?
Effective ventilation of a workshop relies on air exchange and the removal of pollutants to the outside. The easiest way to achieve this is by opening windows or doors that provide natural airflow.
The cutting station should be set up so that the predominant direction of air flow carries the vapors away from the operator and not toward him. Detailed rules security The work includes practical tips for organizing the workplace.
In rooms without the possibility of natural ventilation, it is necessary to use a mechanical exhaust system. The basic set up is an exhaust fan mounted in the window or vent and fresh air supply from the opposite side of the room. The capacity of the fan should provide at least 6-8 times air exchange per hour for the thermal cutting room.
Top rated products
-
Akumulator Procut 21V 4.0Ah Li-Ion
Original price was: € 41,00.€ 38,00Current price is: € 38,00. -
Adapter Minova → Milwaukee
Original price was: € 29,00.€ 24,00Current price is: € 24,00.
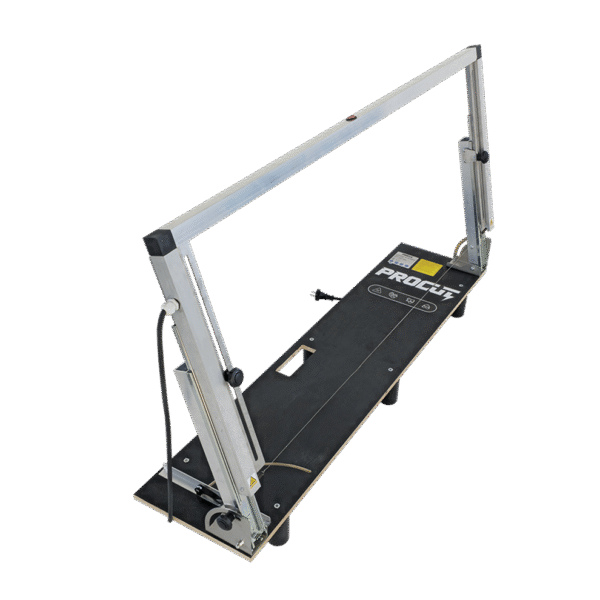
Styrofoam cutting machine with suction system - is it worth it?
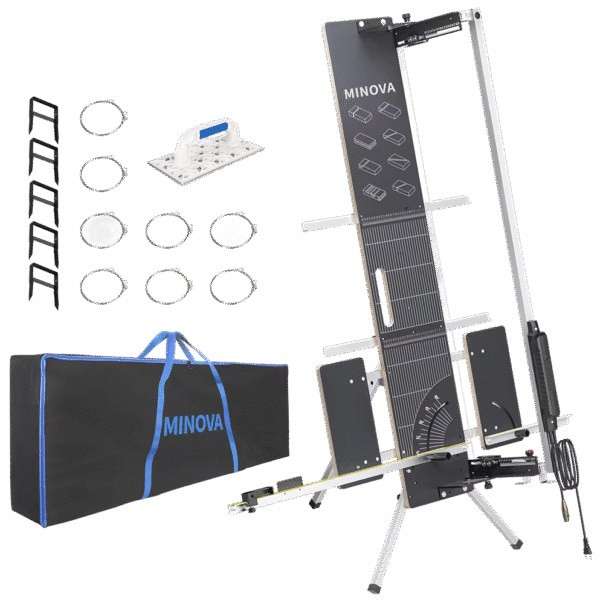
Professional cutters can be equipped with a local vapor extraction system that collects contaminants directly at the site. Minova ELITE professional cutting machine available in our store offers an advanced approach to the topic of occupational health and safety.
Advantages of suction systems:
- Effective vapor removal - Collecting directly at the source before they disperse around the room
- A cleaner stand - less deposits on the device and the environment
- Better working conditions - The operator does not directly inhale the fumes produced during cutting
- Compliance with health and safety regulations - especially important in industrial settings
For workshops involved in intensive polystyrene processing, the investment in an extraction system makes economic sense. Less exposure of operators to fumes translates into better well-being and productivity, and also meets legal requirements for protecting the health of workers.
How to safely set up a thermal knife stand at home?
Thermal knife in a domestic setting requires thoughtful organization of the space. The basic principle is to choose a room with the possibility of effective ventilation - preferably with a window that can be opened while working. The workstation should be positioned close to the window so that the resulting fumes can escape freely.
An additional safety solution is the use of a portable fan aimed at the operator, which discharges fumes toward the window. The fan does not have to be large - a typical desk model placed a meter away from the workstation is sufficient. It is important not to direct the air stream directly at the heated wire or blade, as this can disrupt the cutting process by overcooling.

Cutting with resistance wire in the field - how to ensure safety?
Working on a construction site or in the field presents additional ventilation challenges. The lack of a fixed position and changing conditions require a flexible approach. The basic principle is to perform work in areas with natural air flow - preferably outdoors or in rooms with open windows and doors. Mobile devices They perform perfectly in such conditions.
In enclosed spaces without ventilation, it is a good idea to limit the duration of continuous work and take regular breaks for ventilation. For intensive work lasting several hours a day, consider using a respirator with a FFP2 class dust filter, which reduces the inhalation of fine particles. It does not protect against VOCs, but reduces overall exposure to contaminants.
Filters and purifiers - are they really necessary?
For professional workshops with intensive production, consider investing in an air purifier with a carbon filter. Such a device removes from the air both fine particles and volatile organic compounds responsible for the characteristic odor. Basic accessories to enhance workplace safety also include protective masks and heat-resistant gloves.
FAQ – Najczęściej zadawane pytania dotyczące cięcia styropianu na gorąco
Can I cut Styrofoam in a basement without a window?
Cutting in a basement without a window is possible only with the use of mechanical exhaust ventilation that discharges vapors to the outside, otherwise the concentration of vapors will quickly reach troublesome levels.
At what temperature of Styrofoam cutting is there the least smoke?
The least smoke is produced at 250-300°C, which is optimal for EPS polystyrene, higher temperatures significantly increase fume emissions.
What is the best way to cut Styrofoam in an apartment?
In an apartment, it is best to use the thermal cutter with the window open and the fan on, limiting work sessions to a maximum of 30-40 minutes with breaks for ventilation.
What is the best for cutting Styrofoam without polluting the air?
The most common method is mechanical cutting with a saw or knife, but it generates a lot of dust, thermal cutting at optimal temperature and good ventilation is the best compromise between quality and cleanliness.




